Introduction
Biceps tendonitis is a condition that strikes athletes, fitness enthusiasts, and even those engaged in routine physical activities. Characterized by pain and tenderness in the front of the shoulder or upper arm bone, it can significantly impact one’s quality of life and ability to perform everyday tasks. Fortunately, physical therapy offers hope, providing relief and rehabilitation to those suffering from this ailment through a tailored combination of exercises, manual therapies, and innovative treatment approaches.
Physical therapy not only addresses the symptoms but also targets the underlying causes of biceps tendonitis. This blog delves deep into the world of physical therapy treatments for biceps tendonitis, guiding you through understanding the condition, recognizing symptoms of biceps tendinitis, and exploring effective treatment strategies to restore strength and mobility.
Understanding Biceps Tendonitis
What is Biceps Tendonitis?
Biceps tendonitis is an inflammatory condition affecting the tendon that attaches the biceps muscle to the bones in the shoulder and elbow. The hallmark of this condition is pain, which is often worsened by lifting, pulling, or repetitive motion or movements of the arm. Understanding what biceps tendonitis is crucial for those seeking relief, as it lays the foundation for effective treatment strategies.
The inflammation typically results from overuse, leading to discomfort and limiting functional movement. By identifying the early signs and symptoms, individuals can seek timely intervention, preventing the progression to more severe complications.
Anatomy and Causes of Biceps Tendonitis
The biceps muscle plays a pivotal role in the shoulder and elbow movement, making it susceptible to overuse and injury. The biceps also contribute 10 percent of the total power in shoulder abduction when the arm is in external rotation, highlighting their significance beyond just flexing the elbow. The tendonitis arises when the bicep’s protective tendon sheath becomes irritated, often due to repetitive stress or sudden increases in activity level.
Factors contributing to the development of biceps tendonitis include age-related wear and complete tear, improper lifting techniques, and participation in sports requiring overhead motions, such as tennis or swimming. This intricate involvement of the biceps in various movements underscores the importance of understanding the anatomy and causes of biceps tendonitis, which is essential for developing targeted prevention and treatment plans.
Recognizing Biceps Tendonitis
Common Symptoms and Diagnosis
Identifying biceps tendonitis involves being vigilant about the symptoms and seeking healthcare professional evaluation for an accurate diagnosis. The primary biceps tendonitis symptoms include:
- Pain and Tenderness: The most noticeable symptom is a sharp or dull pain at the front of the shoulder or upper arm, particularly when lifting objects, reaching overhead movements, or even during rest.
- Swelling and Redness: In some cases, the affected area may exhibit signs of swelling or redness, indicating inflammation.
- Strength Loss: Individuals may experience a noticeable decrease in arm strength, making it difficult to carry out daily activities.
- Clicking or Popping Sounds: Movements of the shoulder might be accompanied by clicking or popping sounds, signaling potential tendon damage.
Diagnosis of biceps tendonitis typically involves a thorough physical examination by a healthcare provider. They may perform specific tests to assess the range of motion, strength, and pain response in the shoulder and arm. Imaging tests like MRI or ultrasound can also be used to visualize the extent of inflammation or damage to the tendon. Interestingly, research indicates that the accuracy of unenhanced MRI of the shoulder for detecting bicipital tears was quite high (86%), respectively. This highlights the importance of comprehensive diagnostic approaches, considering both clinical examination and imaging findings, to accurately diagnose and treat biceps tendonitis.
Early recognition and diagnosis of biceps tendon injuries are crucial for preventing further damage and starting an effective treatment plan. Understanding these symptoms enables individuals to take proactive steps toward seeking medical advice and treatment.
Treating Biceps Tendonitis with Physical Therapy
Specific Physical Therapy Treatments
Physical therapy stands out as a cornerstone for the nonsurgical treatment of biceps tendonitis, focusing on relieving severe pain, reducing inflammation, and restoring normal function. Here are specific biceps tendonitis exercises and techniques used in physical therapy:
- Stretching Exercises: Gentle stretching exercises are recommended to improve flexibility and reduce tension in the biceps tendon. This might include shoulder and arm stretches that elongate the biceps muscle and tendon.
- Strengthening Exercises: Gradually introducing strengthening exercises helps rebuild the muscle and tendon strength. This is crucial for regaining functionality and preventing future injuries.
- Manual Therapy: Techniques such as massage and mobilization can be applied by therapists to increase blood flow, reduce pain, and improve the range of motion in the shoulder and elbow.
Each treatment plan is personalized, taking into account the individual’s specific symptoms, lifestyle, and activity level. The goal of physical therapy is not only to alleviate the immediate symptoms but also to equip individuals with the knowledge and exercises needed to prevent recurrence.
Pain Management Techniques
Incorporating pain management techniques within the treatment plan is crucial for enhancing patient comfort and facilitating recovery. Key strategies include:
- Education on Activity Modification: Patients with biceps tendinitis are taught how to adjust their activities to avoid aggravating the tendonitis.
- Therapeutic Modalities: As mentioned, the use of ice, heat, ultrasound, and electrical stimulation plays a significant role in managing pain and inflammation.
- Ultrasound Therapy: A non-invasive treatment that uses sound waves to promote healing and reduce inflammation in the affected bicep tendons.
- Electrical Stimulation: This modality can help manage pain and reduce muscle spasms by delivering mild electrical pulses through the skin.
- Ice and Heat Application: Alternating between ice and heat can help manage pain and inflammation. Ice or cold packs reduce swelling, while heat therapy facilitates blood flow and relaxation of tight muscles.
- Ergonomic Advice: For individuals whose work or daily activities contribute to their condition, physical therapists provide guidance on ergonomic adjustments to reduce strain and risk of biceps tendon injury.
By integrating these techniques, physical therapy not only addresses the physical aspects of biceps tendonitis but also ensures a comprehensive approach to pain management.
Backcountry Physical Therapy Approach to Biceps Tendonitis
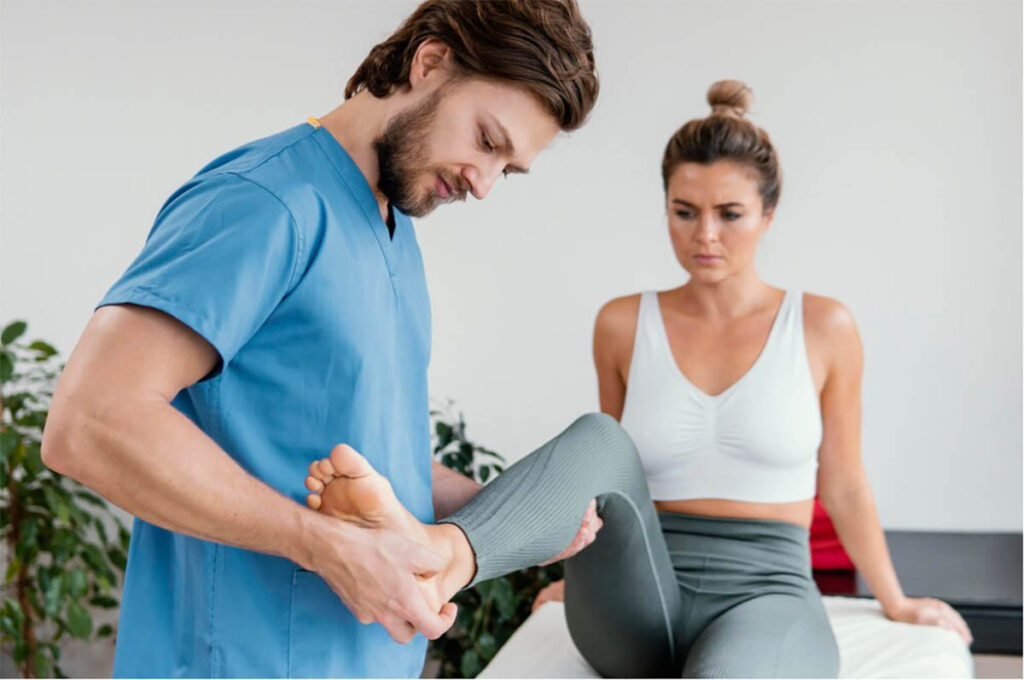

The Backcountry Physical Therapy Approach to Biceps Tendonitis emphasizes a holistic and individualized treatment plan that extends beyond conventional clinic settings, making it an ideal physical therapy for weightlifters and active individuals. This innovative approach integrates outdoor activities and movement workouts, facilitating not only physical healing but also mental well-being. By leveraging the therapeutic effects of nature, patients, including weightlifters, engage in guided exercises and activities tailored to their recovery stage, enhancing motivation and adherence to the treatment plan.
Prevention Strategies
Preventing biceps tendonitis is key to maintaining long-term shoulder and arm health, especially for those at higher risk due to their activities or occupations. Physical therapist offers valuable strategies closely related to prevention, including:
- Regular Stretching and Strengthening: Incorporating daily exercises to maintain flexibility and strength in the biceps and surrounding muscles to bones, reducing the risk of overuse injuries.
- Proper Technique and Posture: Training on the correct techniques and postures for various activities, especially sports and exercises that involve repetitive movements in the arm, is crucial. Working with an athletic trainer can provide personalized guidance to ensure these practices are effectively implemented, reducing the risk of biceps tendonitis.
- Ergonomic Adjustments: Making ergonomic changes to workspaces and equipment to minimize stress on the biceps tendon during daily tasks.
- Activity Modification: Learning to modify activities and take regular breaks to prevent excessive strain on the tendon.
Adopting these strategies can significantly reduce the likelihood of developing biceps tendonitis, empowering individuals to engage in their preferred activities confidently and reducing the risk of injury.
Conclusion
Biceps tendonitis, while painful and potentially debilitating, can be effectively managed and treated with the right approach. Physical therapy plays a pivotal role in this process, offering a range of treatments from specific exercises to innovative pain management strategies like the Backcountry Physical Therapy Approach. By focusing on pain management, prevention strategies, and a holistic treatment option, individuals suffering from biceps tendonitis can achieve significant relief and return to their normal activities. Remember, early recognition and proactive treatment of biceps tendinitis are key to a successful recovery.
FAQs
Is it good to massage bicep tendonitis?
Yes, massage can be beneficial for biceps tendonitis as it helps increase blood circulation, reduce muscle tension, and promote healing. However, it should be performed by a health care provider who understands the condition to avoid worsening the symptoms.
Is heat or ice better for bicep tendonitis?
Both heat and ice have their benefits. Ice is recommended during the initial stages of inflammation to reduce swelling and pain. Heat is beneficial in later stages to improve blood flow and relax muscles. Alternating between the two can be effective.
Should I stretch bicep tendonitis?
Yes, stretching is important for biceps tendonitis recovery, but it should be done gently and within pain-free limits. Stretching helps improve flexibility and reduce tension in the biceps tendon, aiding recovery.



